The intercept has an easy interpretation in terms of probability instead of odds if we calculate the inverse logit using the following formula. The number of possible interaction terms increases exponentially with the number of features.

Logistic Regression Analysis With Interaction Terms Predicting Download Table
Prefer A control true Prefer A control false Prefer B.

. Model mort_10yrref0 age sex race educ 2. To interpret the coefficients we need to know the order of the two categories in the outcome variable. Y β 0 β 1 X 1 β 2 X 2 ε.
In addition although Logistic Regression allows investigation into interaction terms they may prove difficult to interpret. First before you interpret a non-crossover interaction read Wagenmakers et al. Z is said to be the moderator of the effect of X on Y but a X Z interaction also means that the effect of Z on Y is moderated by X.
Logistic regression with an interaction term of two predictor variables In all the previous examples we have said that the regression coefficient of a variable corresponds to the change in log odds and its exponentiated form corresponds to the odds ratio. Y β 0 β 1 X 1 β 2 X 2 β3X1X2 ε. We adopt the view that the effects of time are linear.
One example of this interaction in the insurance context is the premium increases may differ by age. The varieties were both grown on-farm and on-station. Heres what a Logistic Regression model looks like.
This is only true when our model does not have any interaction terms. In your case this would be just 4 probabilities. E β 0 1 e β 0 e-193 1 e-193 013 so.
Interactions with Logistic Regression. This type of plot displays the fitted values of the dependent variable on the y-axis while the x-axis shows the values of the first independent variable. Table 12 shows that adding interaction terms and thus letting the model take account of the differences between the countries with respect to birth year effects on education length increases the R 2 value somewhat and that the increase in the models fit is statistically significant.
The best way to understand these effects is with a special type of line chart an interaction plot. We suggest two techniques to aid in interpretation of such interactions. An interaction occurs if the relation between one predictor X and the outcome response variable Y depends on the value of another independent variable Z Fisher 1926.
The most straightforward way to do this is to create a table of the outcome variable which I have done below. Researchers need to decide on how to conceptualize the interaction. I The simplest interaction models includes a predictor variable formed by multiplying two ordinary predictors.
The probability of success or the presence of an outcome. Meanwhile the various lines represent values of the second independent variable. 1 numerical summaries of a series of odds ratios and 2 plotting predicted probabilities.
And if the interaction term is statistically significant associated with a p-value 005 then. Just like in a general linear model analysis where the coefficient for an interaction term does not have a slope interpretation when an interaction effect is included in a multiple logistic regression model the odds ratios ORs based on coefficient estimates are not all meaningful and the correct ORs to report need to be recalculated. My own preference when trying to interpret interactions in logistic regression is to look at the predicted probabilities for each combination of categorical variables.
There are some discussion on 3. β 3 can be interpreted as the increase in effectiveness of X 1 for each 1 unit increase in X 2 and vice-versa. 3 would test 3-way interactions such as agesexrace.
Logit p a bX₁ cX₂ Equation You notice that its slightly different than a linear model. Adding log-odds ratios of all the predictors participating in the particular interaction to the interaction coefficient reported by the model gives us a real log-odds ratio of an interaction. Logistic interactions are a complex concept Common wisdom suggests that interactions involves exploring differences in differences.
The following code simulates events deaths from a known model for two groups over three time points. The pipe symbol tells SAS to consider interactions between the variables and then the 2 tells SAS to limit it to interaction level between 2 variables. So we have deaths acorss two groups 0 control 1 treatment at three time points 0 baseline 1 1 year in 2.
Second if youre working with binary data and you predict a non-crossover interaction in a logistic model be aware that a significant interaction in terms of the log-odds output by your model neednt correspond to an interaction in terms of. In that case by interacting them you explore the impact that the IV has on the DV only in the cases. LogitPY 1 0 1 X 1 2 X 2 3 X 1 X 2 I Interaction term 2.
Interpreting Interaction Terms in a GLM Binomial family logit link - Logistic Regression. 05 Sep 2017 0837. Dear Statalist members I am not entirely sure of how to interpret the coefficients especially of the interaction term from the ordinal logistic regression that I ran.
If the differences are not different then there is no interaction. Interpreting results of regression with interaction terms. Lets clarify each bit of it.
Particularly a log-odds ratio of the interaction sexmalepassengerClass2nd -39848 - 12666 01617 -50897. Logit p is just a shortcut for log p1-p where p P Y 1 ie. Interpretation of the effect of X 1 depends on the value of X 2 and vice versa.
There are four variables have significant interaction effects in my logistic regression model but I still did not get good way to interpret it through R software. I Exactly the same is true for logistic regression. The intercept is β 0 -193 and it should be interpreted assuming a value of 0 for all the predictors in the model.
You can specify interaction terms in the model statement as. In my trials farmers have rated 5 different maize varieties on different characteristics. But in logistic regression interaction is a more complex concept.
How to interpret the intercept. Newsletter focuses on how to interpret an interaction term between a continuous predictor and a categorical predictor in a logistic regression model. The interpretation of the interaction is quite simple when one of the two variables is a dummy.

How To Interpret An Interaction Effect In Logistic Regression Models
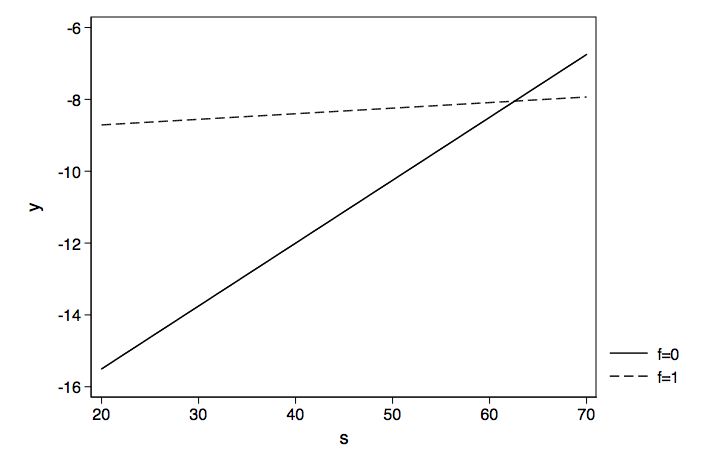
Deciphering Interactions In Logistic Regression
57 Interactions In Logit Regressions Why Positive May Mean Negative Data Colada
Jan Vanhove Interactions In Logistic Regression Models

Logistic Interpreting Interaction Terms And Main Effects In Logit Regression With Multiple Dummy Variables Cross Validated
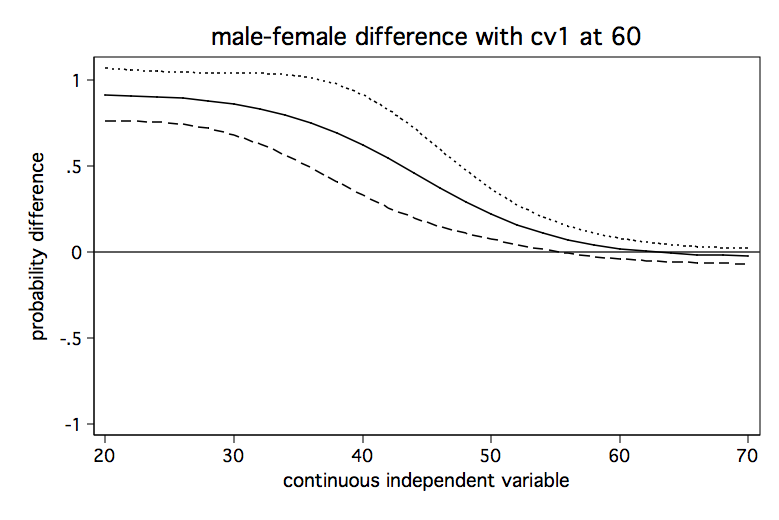
Deciphering Interactions In Logistic Regression

3 Logistic Regression Using Spss Pasw Example 2 Interaction Terms Youtube
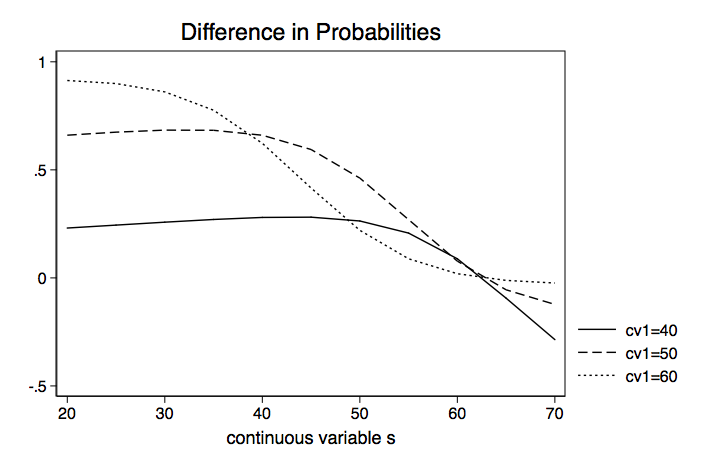
0 comments
Post a Comment